Color Terminology | Fundamentals of Design
Color is a deceptively complicated design concept. In order to fully master color we need to all be on the same terms.
Terms
Hue
A hue is the most dominant wavelength independent of chroma and saturation. Red, blue, green, etc. are all examples of hue.
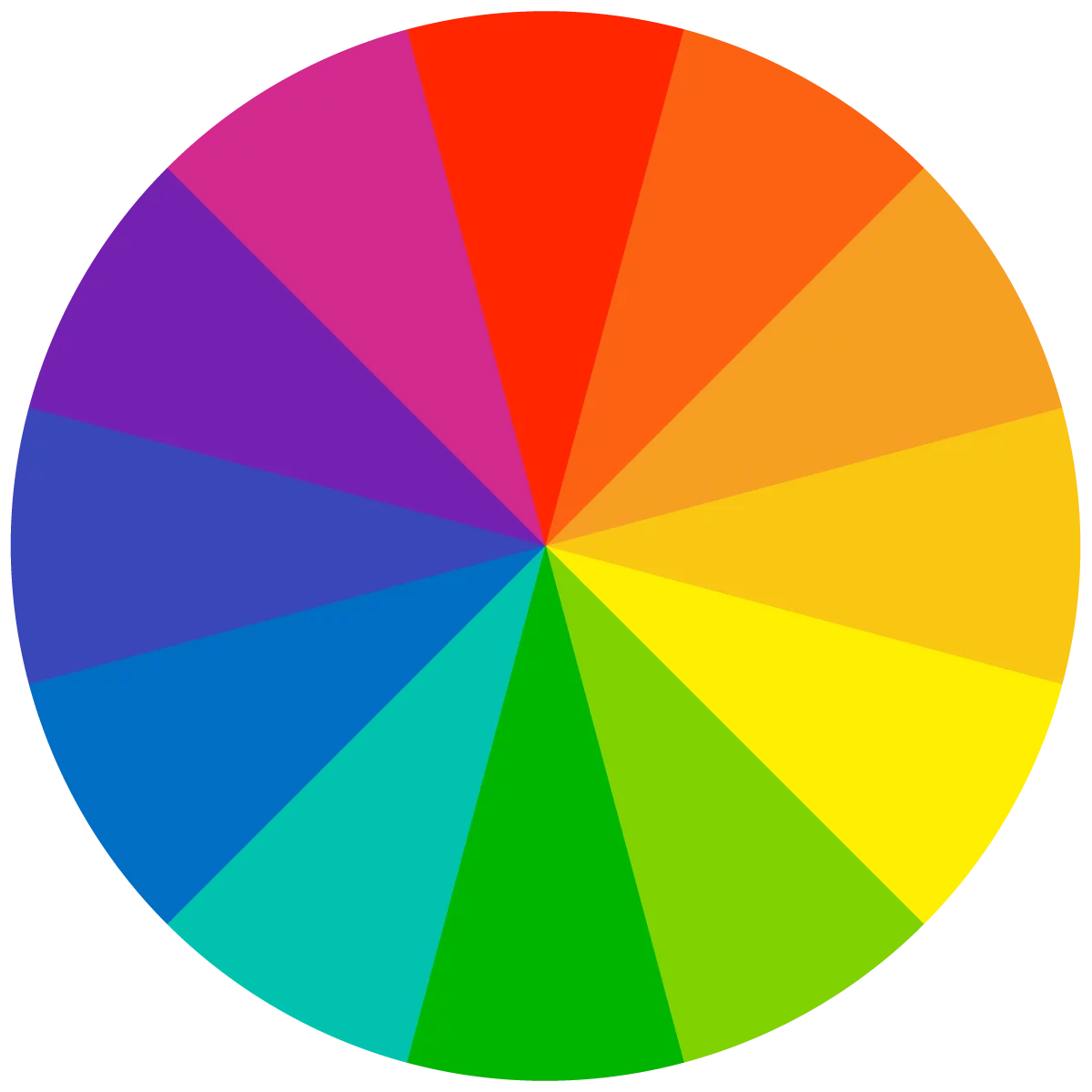

Saturation
Saturation is the intensity/purity of the color and is interchangeable with chroma. Adding in black, white, or grey reduces the saturation of a hue.
Chroma
Chroma relates to the purity of the color. Adding in black, white, or grey reduces the chroma of a hue. In design utilize either colors with the same chroma, or colors with chroma that is a few steps away from each other.
Value
Also known as brightness, value refers to how light or dark a color is. The lighter the color, the higher the value.

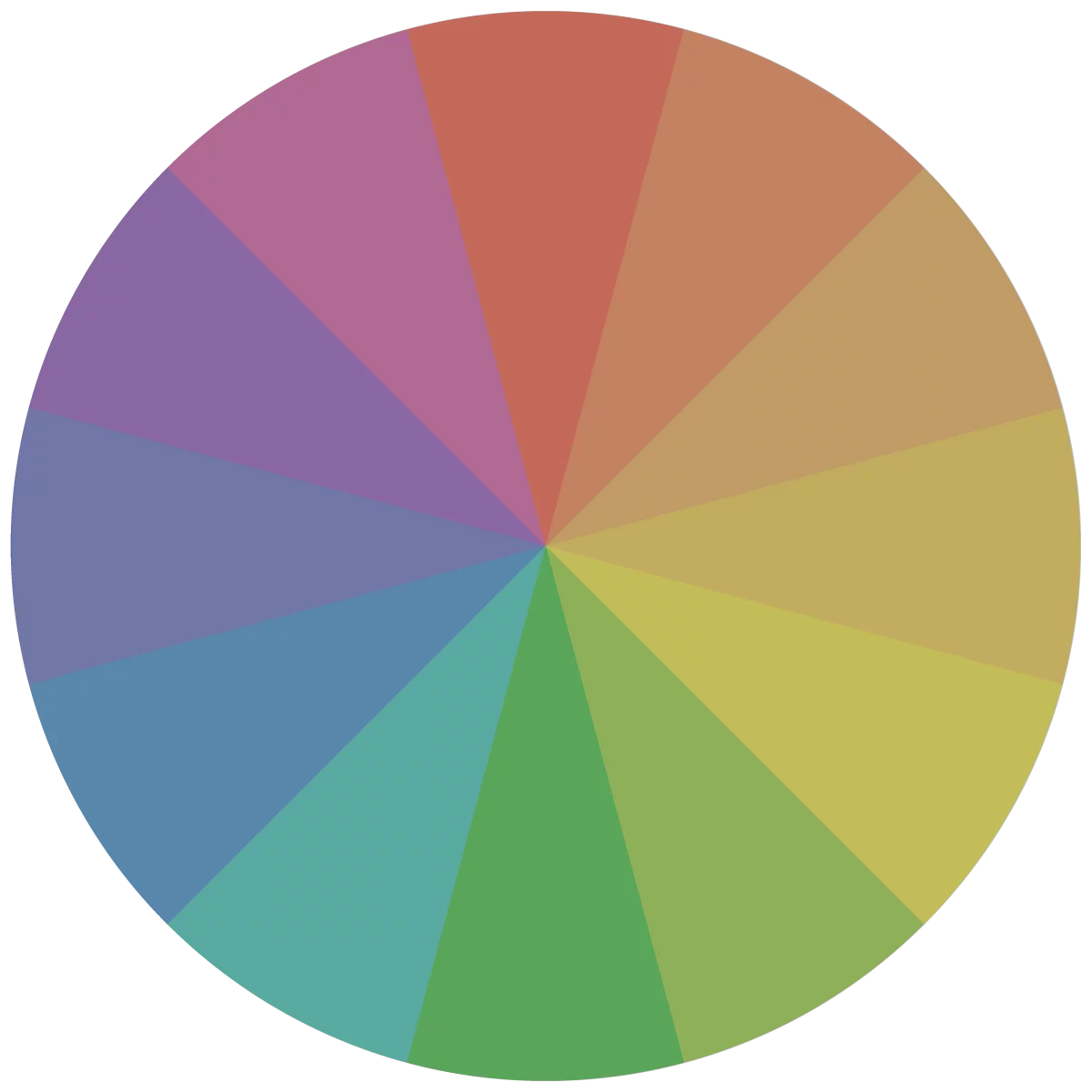
Tones
Adding grey into a color to form a new color creates a “tone”. Tones are generally softer than their pure hues. Utilizing a variety of tones can add to a level of sophistication if used properly.
Shades
The addition of black into a color to make it darker creates a shade. Shades can take the place of black within designs to avoid having a design that is too dark. Shades can also be utilized in place of a neutral.
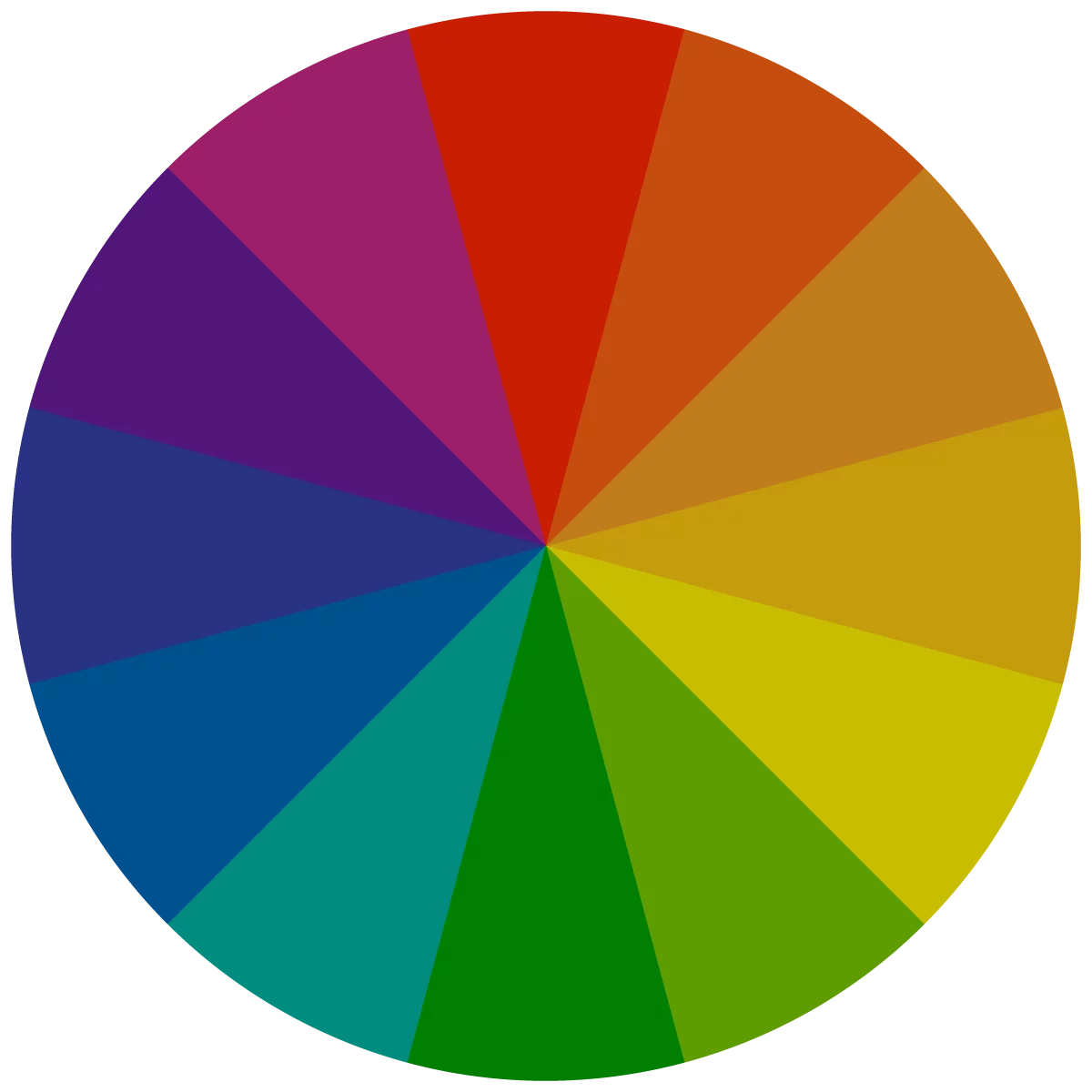
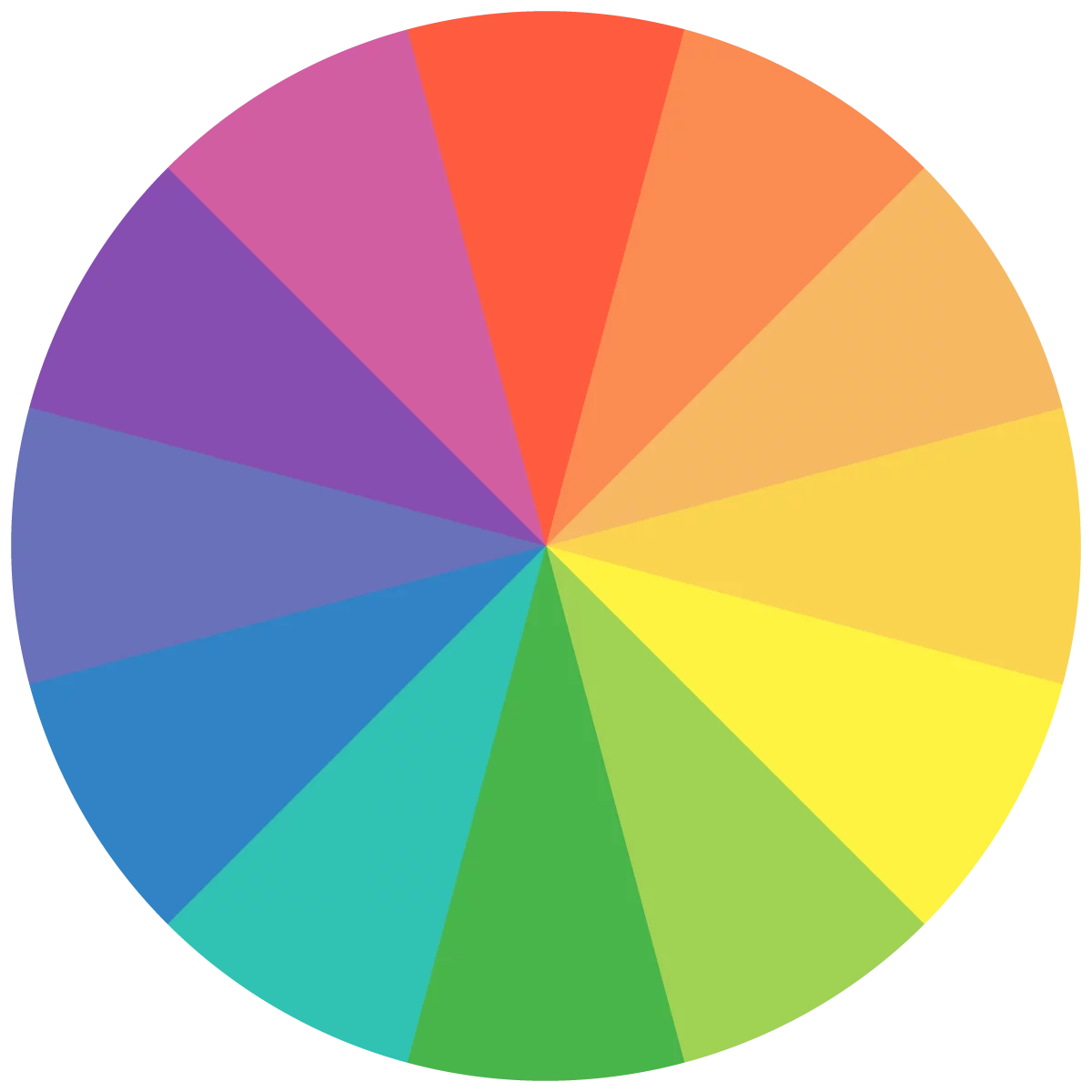
Tint
A tint is the addition of white into a color to make it lighter. Tints can take the place of white in order to keep a design from feeling to light. Tints can also be used in place of neutral colors as well.
Color Space
Color space is a set of numbers given to specific color values that when mixed reproduce a wide array of colors. There are two main forms of color space: RGB and CMYK.
RGB
RGB is the default color space for web and computer graphics. Utilizing the colors Red, Green, and Blue in an additive color system. With 256 levels per color can create 16,777,216 colors. You may be asking yourself, why not red, blue and yellow. Well the photoreceptors in the human eye do use red and blue, they also use green and omit yellow and are known as trichromatic vision.
Additive Color
Additive color is the idea that you are adding light to get color. This is how a monitor works, you’re turning up the levels of red, blue, and green in order to receive a brighter image. When you combine all the colors together you get white.


CMYK
CMYK is the default color space for 4 color process printing. CMYK utilizes cyan, magenta, yellow, and black in order to create colors in a subtractive system. Color in CMYK goes across a percentage spectrum of 0-100. The CMYK printing process utilizes small dots in combination with each other to reproduce various mixes of color. Colors in the RGB space may not be possible within the CMYK space, so be cognisant of this when designing for print.
Subtractive Color
Subtractive color is the idea that as you add in color, light is subtracted from the medium. Think of when you are playing with crayons as a kid. Combining all the colors in a subtractive color space creates black, while white is the absence of color.
Spot Colors
A spot color is a special premixed ink that requires its own print plate on a press. This differs from process coloring in that no mixing occurs during the printing process. Spot colors provide consistency and can provide more detailed and vibrant color. Some colors don’t fall within the CMYK range or accuracy is key (with logos or other color-specific elements). Spot Colors also can provide special effects such as metallics or fluorescence as well as provide a more even coverage over a larger surface.
Pantone
Created in 1963, Pantone colors are a system of colors matched with printed inks. The need was filled due to printers and designers not getting the same colors. This is a first-party, standardized color system used across many industries which utilizes a unique number to describe a color. Pantone breaks colors into two categories
- Print and Packaging
- Fashion and Product Design
Color can increase brand recognition by 87% and sell more effectively 50-85% of the time so getting the color right is an important point.

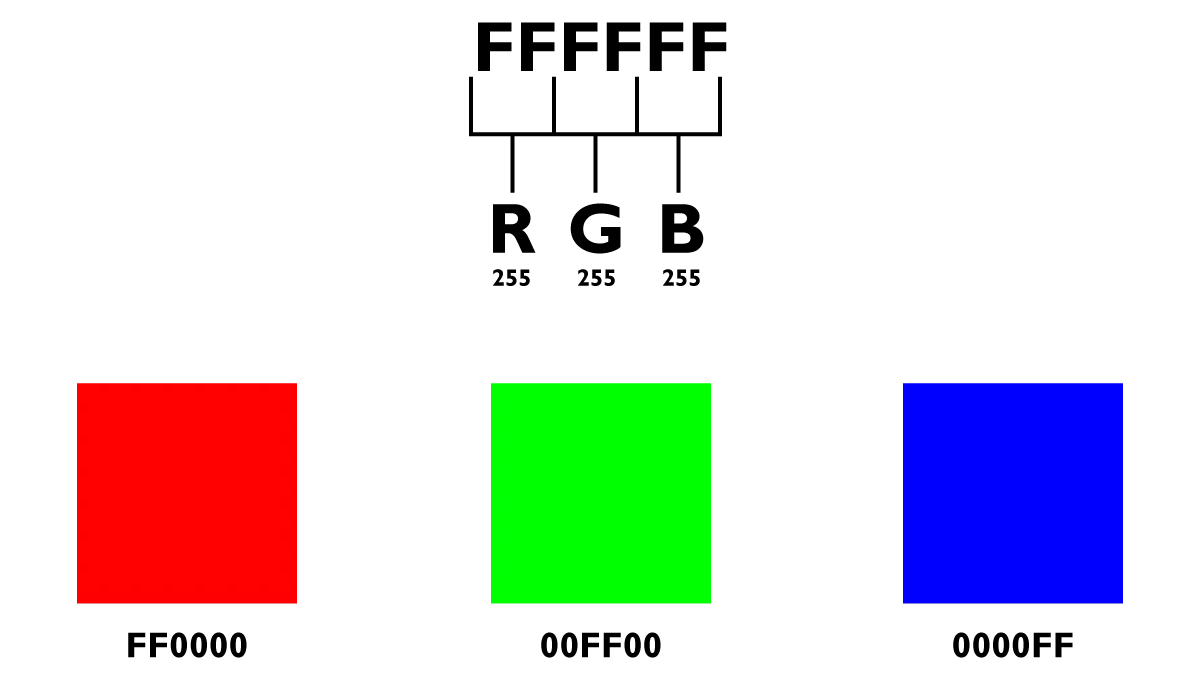
Hex Code
What is a hex code? A hex code is a six digit code of letters and numbers that represent an RGB color traditionally used in web development and in design. This allows for website code to easily refer to what color to display on a site without having to individually type out the r, g, and b values.
Conclusion
Color theory is a complex concept. As we covered in our Introduction to Color article, color can give a design feeling. As we continue we will cover color schemes and then move deeper into the intricacies of color.





