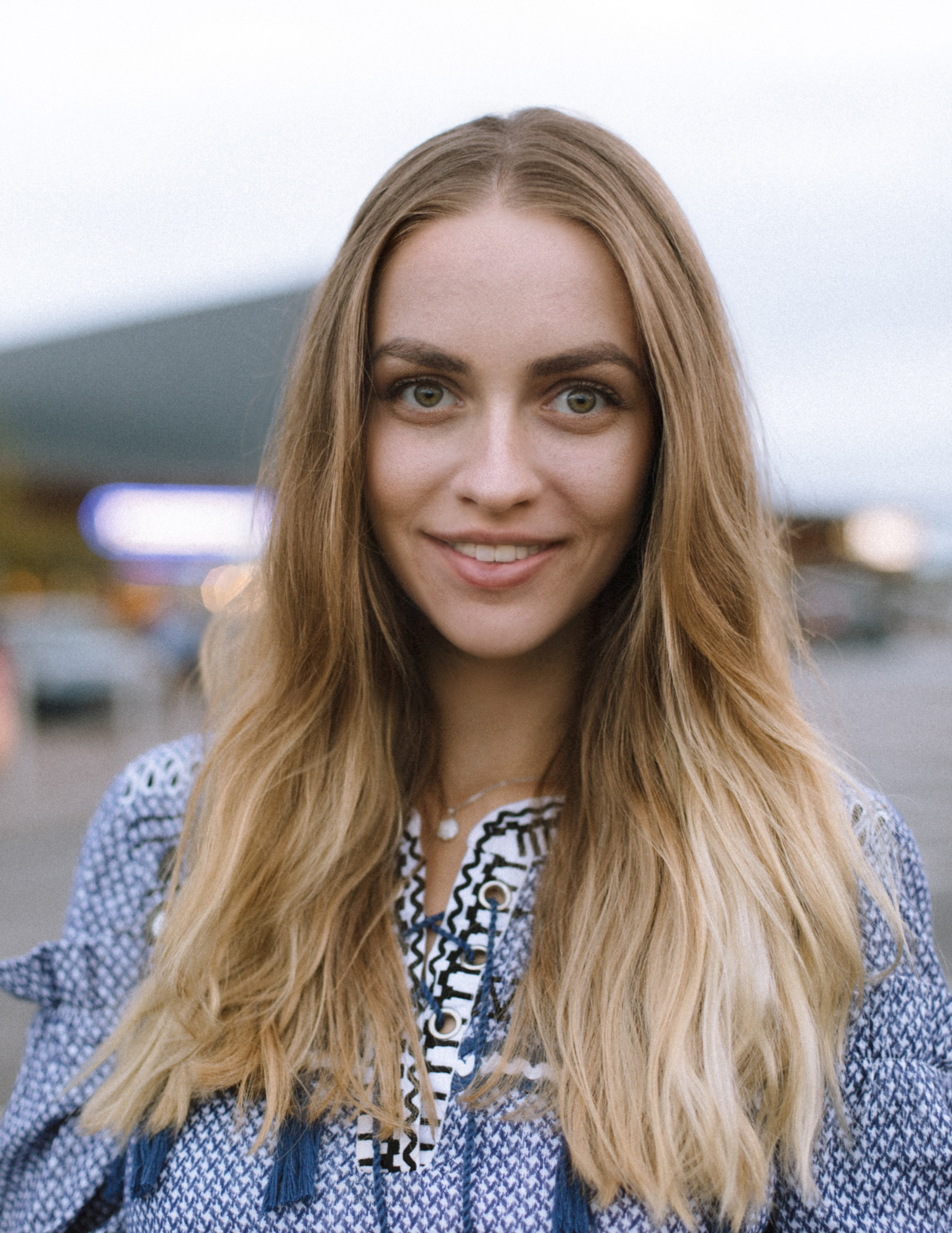
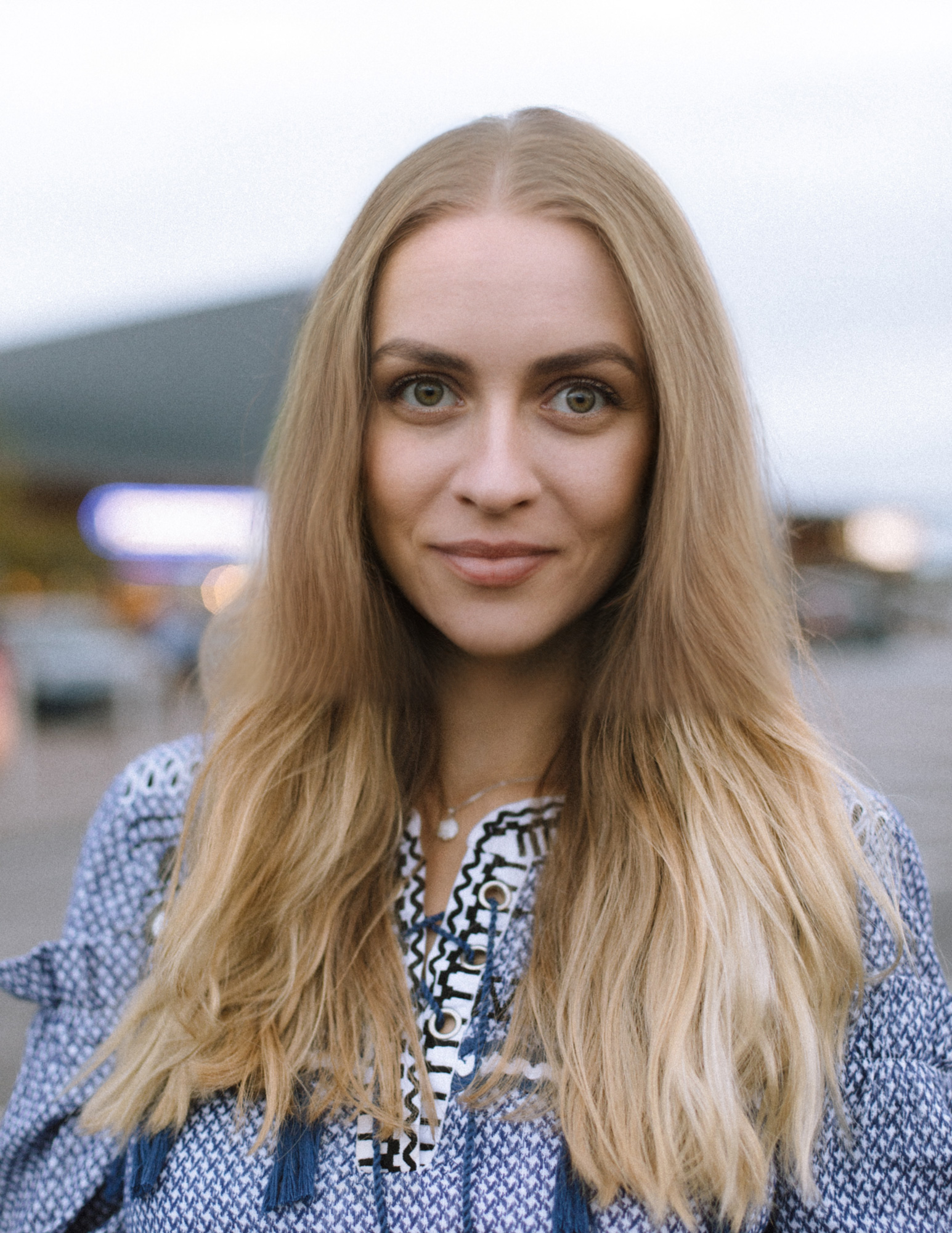
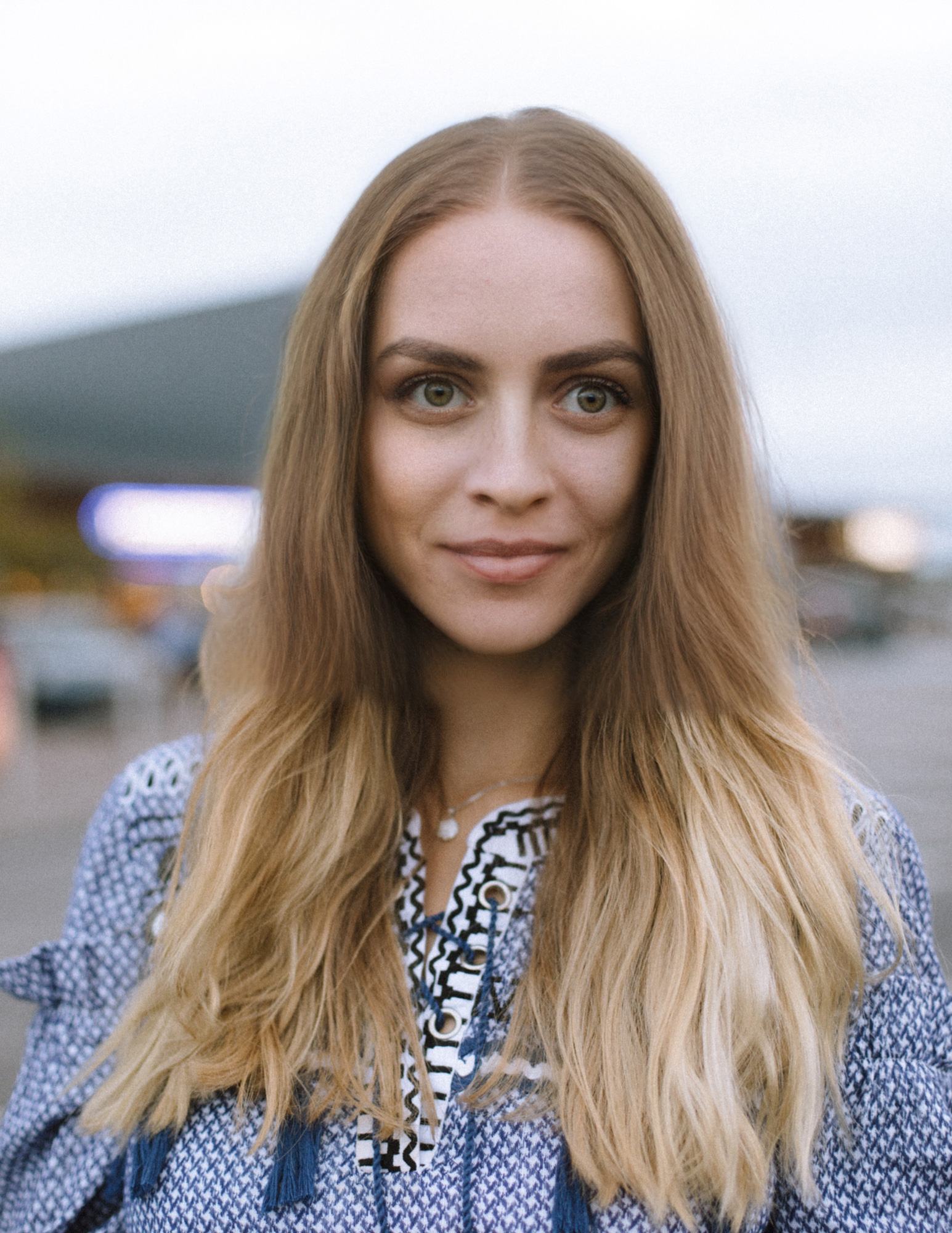
How to Use the Smart Portrait Neural Filter | Adobe Photoshop Tutorial
With the release of Adobe Photoshop 22.0 in October 2020 Adobe released the Smart Portrait beta neural filter. This filter is revolutionizing the photo-editing process in ways that some have found disconcerting. From adding teeth to years on someone’s life Sensei powered Smart Portrait has a range of powerful capabilities that we will dive into in this tutorial.
How to Use Smart Portrait
The Smart Portrait Neural Filter can be accessed via the following steps.
1. Open the Image
Open a Photoshop document and select an image to use for the filter. This filter requires a person be in the photo.
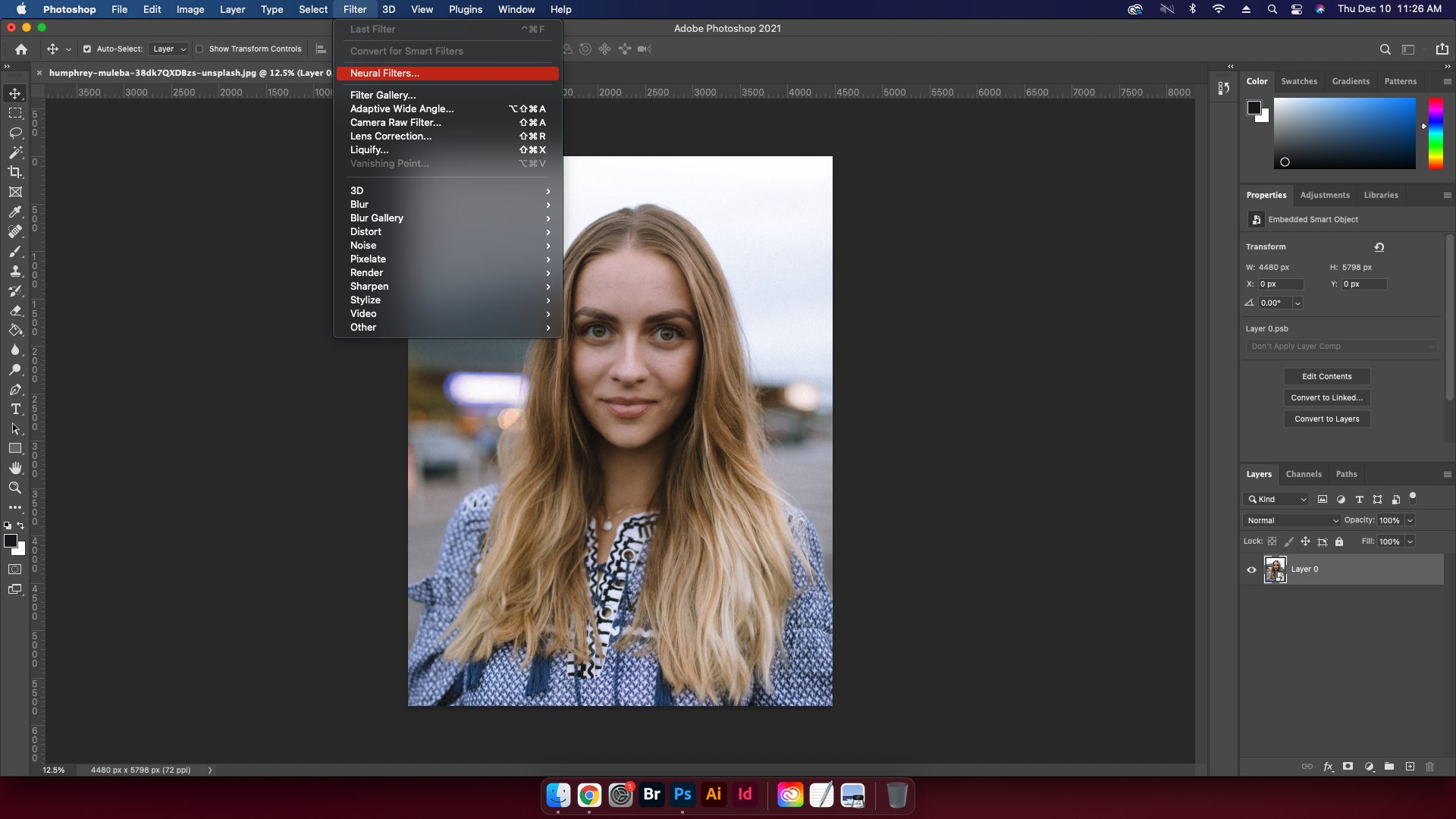
2. Accessing Neural Filters
Go up to the top and select Filter > Neural Filters
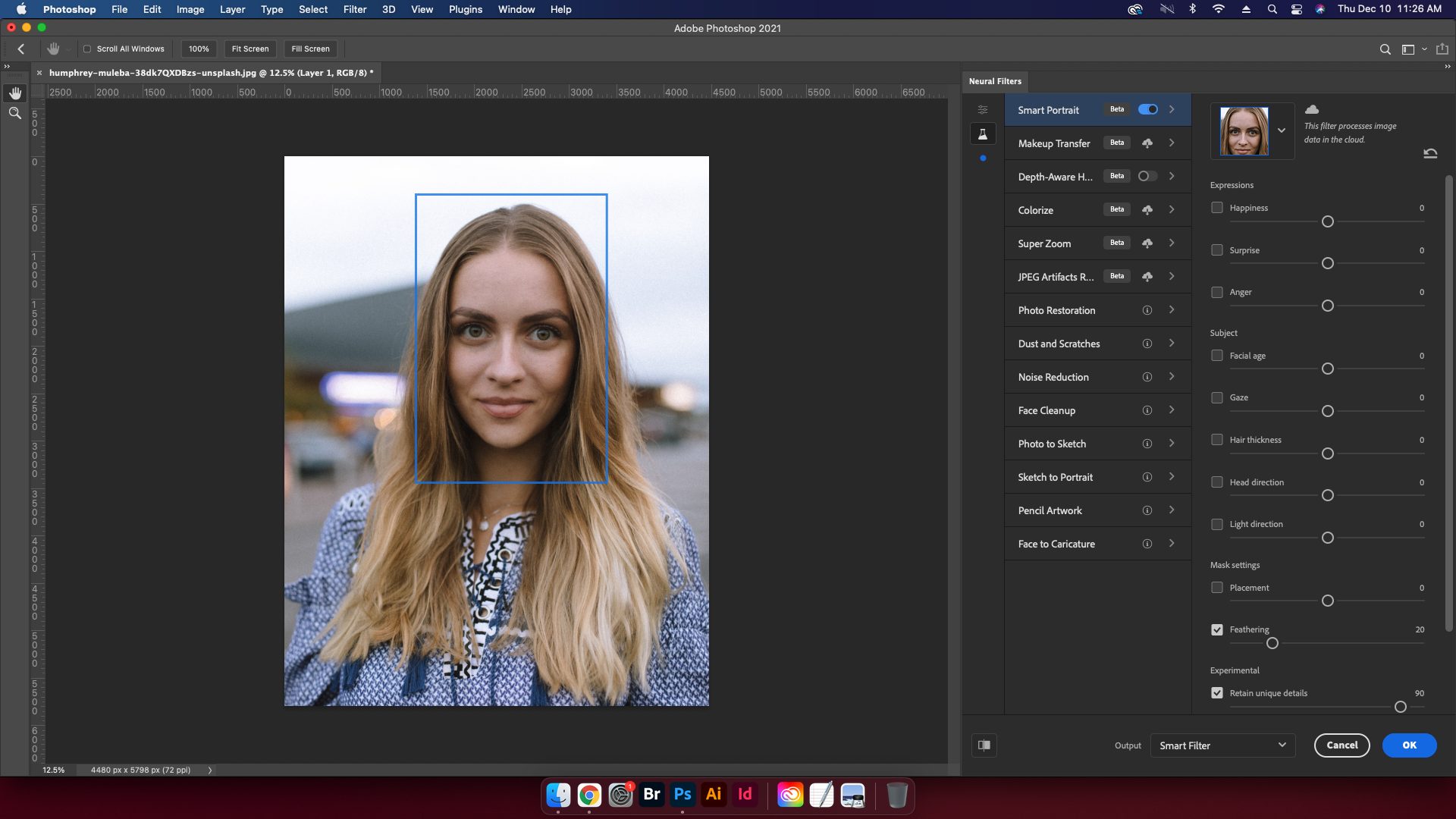
3. Select Smart Portrait
The Neural Filters panel will load on the right side of Photoshop. Select Smart Portrait from the Beta Filters list
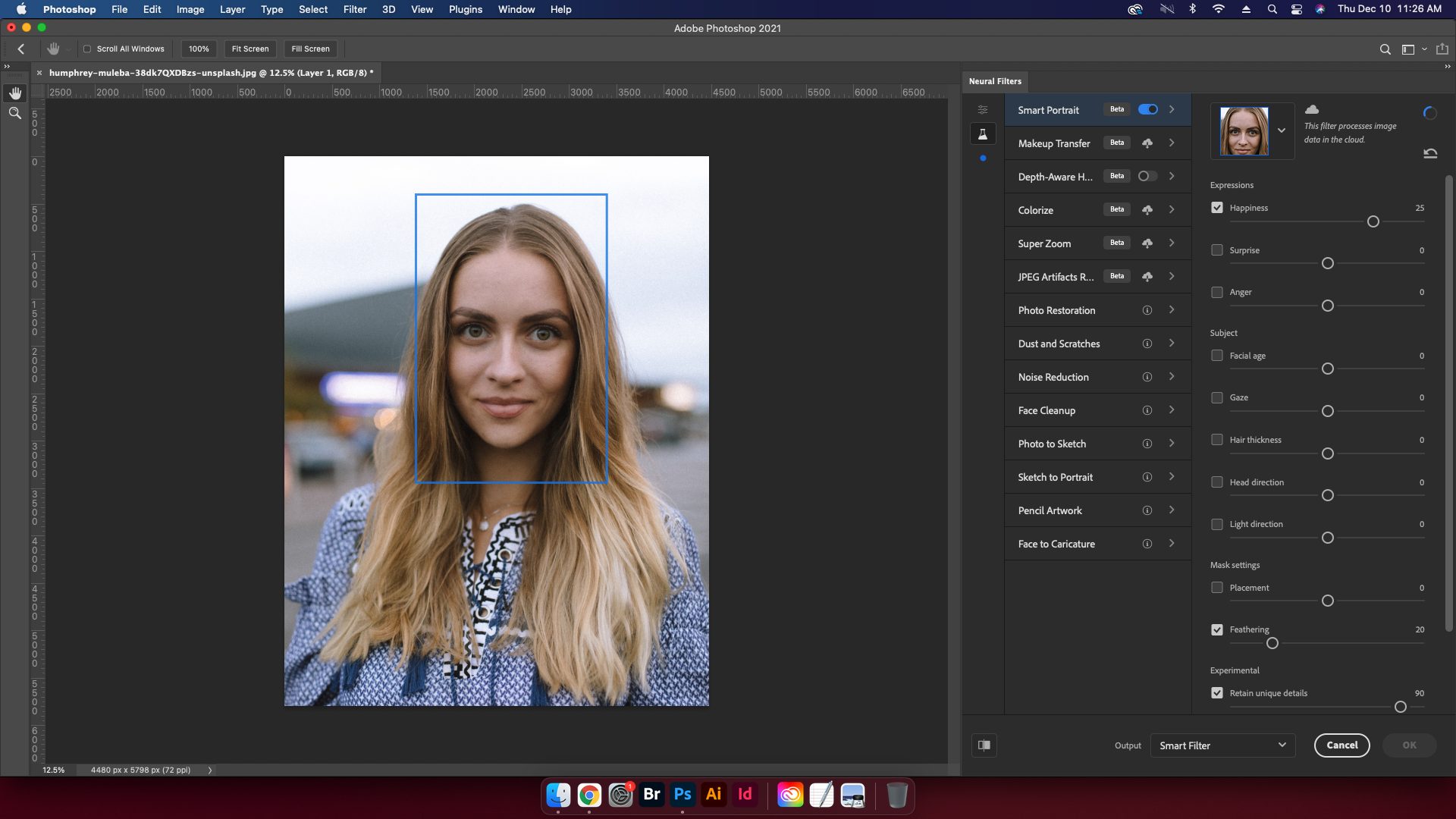
4. Adjust Settings
Adjust the desired settings to get the image you are happy with. The individual controls are covered below.
5. Select Output Method
Select the correct output method desired and then click OK.

Controls
Expressions
Expressions use sliders to make people look as if they’re happy, surprised, or angry to change the facial expression of the subject. For the purposes of this tutorial all have been set to a value of 25.
Happiness
Using the happiness control, one can make a subject appear to be more joyful based on a -50 to 50 scale. Working the slider to the right adds things like a smile to the model.
Surprise
Also based on a similar -50 to 50 scale, the surprise control adjusts features on the model to make them appear more surprised.
Anger
The anger control adds or removes features of the expression based on a -50 to 50 scale. This will include furled brows, narrowing eyes, and if big enough, open mouth as if yelling.
Subject
Facial Age
This slider will change the perceived age of the subject. An increase to the right side of the slider will make the subject appear older while moving the slider to the left will make the subject appear younger.
Gaze
The gaze slider adjusts where the subject’s eyes are positioned. Sliding the gaze to the right will make the subject appear as if they are looking to the right side of the frame.
Hair Thickness
Hair thickness controls what it says, how thick the hair of the model appears. Left on the slider removes thickness while moving the slider to the right adds to the hair thickness.
Head Direction
Head direction controls where the figure’s head is turned. Increasing the value moves the head toward the right of the image while decreasing the value moves the head to the left.
Light Direction
Light direction is controlled on a -50 to 50 scale and sets where the main source of light in the portrait is located. Lighting will adjust on the photo according to the value set so for example let’s say the sun is off to the right of the subject in a composite, add a positive value to the light direction and it will appear as if the sun is shining on the subject.
Mask Settings
Placement
Controls the placement of the mask itself, generally I would recommend only touching this control if you created your own mask for the filter as it can cause some issues with the end result.
Feathering
This filter controls the amount of feathering within the mask selection. Usually this is pretty accurate but if need be the control is available to the user.
Experimental
Retain Unique Details
Retaining the unique details of the model can be key, after all it is what makes them them. By default this is set at 90% to preserve most of the model’s features while still allowing for the Sensei powered algorithms the freedom to make choices to control the changes.
Conclusion
Smart Portrait is a revolutionary new filter that while it has its flaws has found a way into my workflow. Subtlety is the art in question when using this filter to just add a bit more spice to the image. While you’re here, check out our other articles on the 22.0 update: Neural Filters, Sky Replacement, and Pattern Preview.













